2022-02-15 00:00:00 +0000 - Written By Omprakash
What is Sorting?
Arranging all the elements of a given array/list in an ascending order is termed as sorting.
Now we have various Sorting techinques to do so (i.e sort the given array/list)
-
Selection Sort
-
Insertion Sort
-
Bubble Sort
-
Merge Sort
-
Quick Sort
Each of these are different sorting algorithm, with varing time and space complexity.
In sorting algorithms time complexity signifies the number of comparision that are performed to find the correct position of an element in an array.
Selection Sort
It is one of the Greedy algorithm, in which we find minimum element in every swap.
Algorithm:
- Start iterating through the given array form Zero to last index.
- In each iteration find the minimum element between index < iteration number <= last index.
- Swap the minimum with element at index == iteration number.
After first iteration smallest element will be at its correct position (i.e index = 0).
Time complexity: o(n*n) (for all best, average and worst case.)
Space complexity: o(1)
Selection sort performs minimum number of swaps to sort a given array. (n-1) swaps that is o(n).
Insertion Sort
Algorithm:
- Start iterating through the given array from index 1 to last index.
- In each iteration check whether there exists a smaller element at index < iteration number or not.
- If YES swap the elements and repeat step 2.
- If NO continue iteration.
Time complexity:
o(n) -- For Best case, that is given array is already sorted in ascending order.
o(n*n) -- For Average and worst case.
Space complexity: o(1)
Preferred when given array is partially sorted.
Bubble Sort
Algorithm:
- Start iterating through the given array form Zero to one less last index.
- For each iteration, start second iteration form Zero to one less last index.
- Keep swaping the elements if array[i] > array[i+1] in second iteration.
After first iteration largest element will be at its correct position (i.e index = n-1).
Time complexity:
o(n) -- For Best case, that is give array is already sorted in ascending order.
o(n*n) -- For Average and worst case.
Space complexity: o(1)
Merge Sort
Merge sort follows divide and conquer strategy, in which first we divide the array into smaller array’s, sort those smaller arrays and finally merge them together to get our original array in ascending order.
Time complexity: o(n*logn) – For Best, Average and worst case.
Space complexity: o(n)
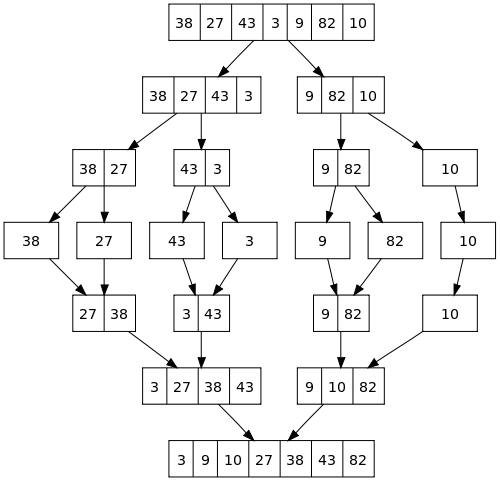
Preferred to used when order of incoming (intial ordering) elements is unknown.
Quick Sort
Quick sort is also an one of the divide and conquer strategy.
- First we select an element, called as pivot element.
- Find the correct position of pivot element by positioning all the smaller and larger elements to pivot’s left and right side repectively.
- Now, Repeat Step-1 and Step-2 for array elements at left and right to the pivot.
Time complexity:
o(n*logn) -- For Best, Average.
o(n*n) -- For worst case, when array is already sorted.
reversed sorted or all elements are same.
Space complexity: o(1)
In quick sort when Pivot is selected at the middle index then it gives best case time complexity.
Stable/UnStable sorting algorithm
A Sorting algorithm is said to be stable if it maintains the relative ordering of non-distinct(same) elements, if not so algorithm is unstable.